

Experience outstanding online performance through Responsive web design Parramatta Our expert team specialises in delivering solutions that improve rankings, drive engagement, and generate valuable leads for consistent business growth in Parramatta
Choose excellence in digital marketing with Small business SEO Parramatta Our proven approaches drive website traffic, enhance customer engagement, and significantly improve conversion rates, supporting long-term business success in Parramatta
Take your digital presence further with Web development Parramatta We develop custom strategies aimed at increasing your online visibility, improving search engine rankings, and achieving sustainable growth for your Parramatta-based business
Best SEO Agency Parramatta Australia.Choose excellence in digital marketing with SEO consultant Parramatta Our proven approaches drive website traffic, enhance customer engagement, and significantly improve conversion rates, supporting long-term business success in Parramatta
Choose excellence in digital marketing with Website designers Parramatta Our proven approaches drive website traffic, enhance customer engagement, and significantly improve conversion rates, supporting long-term business success in Parramatta
Choose excellence in digital marketing with SEO company Parramatta Our proven approaches drive website traffic, enhance customer engagement, and significantly improve conversion rates, supporting long-term business success in Parramatta
Effective Web Design Parramatta Sydney.Take your digital presence further with Web design company Parramatta We develop custom strategies aimed at increasing your online visibility, improving search engine rankings, and achieving sustainable growth for your Parramatta-based business
Choose excellence in digital marketing with SEO audit Parramatta Our proven approaches drive website traffic, enhance customer engagement, and significantly improve conversion rates, supporting long-term business success in Parramatta
Choose excellence in digital marketing with Parramatta web developers Our proven approaches drive website traffic, enhance customer engagement, and significantly improve conversion rates, supporting long-term business success in Parramatta
SEO Packages Parramatta .

Experience outstanding online performance through Professional SEO Parramatta Our expert team specialises in delivering solutions that improve rankings, drive engagement, and generate valuable leads for consistent business growth in Parramatta
Choose excellence in digital marketing with Parramatta WordPress developers Our proven approaches drive website traffic, enhance customer engagement, and significantly improve conversion rates, supporting long-term business success in Parramatta
Maximise your business potential with Technical SEO Parramatta We deliver impactful strategies designed to boost your brand awareness, improve online visibility, and generate a steady flow of qualified leads in Parramatta
Maximise your business potential with SEO for trades Parramatta We deliver impactful strategies designed to boost your brand awareness, improve online visibility, and generate a steady flow of qualified leads in Parramatta
Maximise your business potential with Mobile-friendly web design Parramatta We deliver impactful strategies designed to boost your brand awareness, improve online visibility, and generate a steady flow of qualified leads in Parramatta
Take your digital presence further with Lead generation Parramatta We develop custom strategies aimed at increasing your online visibility, improving search engine rankings, and achieving sustainable growth for your Parramatta-based business


Maximise your business potential with Parramatta SEO packages We deliver impactful strategies designed to boost your brand awareness, improve online visibility, and generate a steady flow of qualified leads in Parramatta
Choose excellence in digital marketing with On-page SEO Parramatta Our proven approaches drive website traffic, enhance customer engagement, and significantly improve conversion rates, supporting long-term business success in Parramatta
Choose excellence in digital marketing with SEO and web design Parramatta Our proven approaches drive website traffic, enhance customer engagement, and significantly improve conversion rates, supporting long-term business success in Parramatta
Transform your business growth with SEO content writing Parramatta Our strategies enhance visibility, attract targeted traffic, and maximise conversions for sustained success Partner with us for measurable digital marketing outcomes today
Take your digital presence further with Parramatta branding and web design We develop custom strategies aimed at increasing your online visibility, improving search engine rankings, and achieving sustainable growth for your Parramatta-based business
Choose excellence in digital marketing with Website optimisation Parramatta Our proven approaches drive website traffic, enhance customer engagement, and significantly improve conversion rates, supporting long-term business success in Parramatta


| Semantics | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||
| Semantics of programming languages |
||||||||
|
||||||||
The Semantic Web, sometimes known as Web 3.0 (not to be confused with Web3), is an extension of the World Wide Web through standards[1] set by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). The goal of the Semantic Web is to make Internet data machine-readable.
To enable the encoding of semantics with the data, technologies such as Resource Description Framework (RDF)[2] and Web Ontology Language (OWL)[3] are used. These technologies are used to formally represent metadata. For example, ontology can describe concepts, relationships between entities, and categories of things. These embedded semantics offer significant advantages such as reasoning over data and operating with heterogeneous data sources.[4] These standards promote common data formats and exchange protocols on the Web, fundamentally the RDF. According to the W3C, "The Semantic Web provides a common framework that allows data to be shared and reused across application, enterprise, and community boundaries."[5] The Semantic Web is therefore regarded as an integrator across different content and information applications and systems.
The term was coined by Tim Berners-Lee for a web of data (or data web)[6] that can be processed by machines[7]—that is, one in which much of the meaning is machine-readable. While its critics have questioned its feasibility, proponents argue that applications in library and information science, industry, biology and human sciences research have already proven the validity of the original concept.[8]
Berners-Lee originally expressed his vision of the Semantic Web in 1999 as follows:
I have a dream for the Web [in which computers] become capable of analyzing all the data on the Web – the content, links, and transactions between people and computers. A "Semantic Web", which makes this possible, has yet to emerge, but when it does, the day-to-day mechanisms of trade, bureaucracy and our daily lives will be handled by machines talking to machines. The "intelligent agents" people have touted for ages will finally materialize.[9]
The 2001 Scientific American article by Berners-Lee, Hendler, and Lassila described an expected evolution of the existing Web to a Semantic Web.[10] In 2006, Berners-Lee and colleagues stated that: "This simple idea…remains largely unrealized".[11] In 2013, more than four million Web domains (out of roughly 250 million total) contained Semantic Web markup.[12]
In the following example, the text "Paul Schuster was born in Dresden" on a website will be annotated, connecting a person with their place of birth. The following HTML fragment shows how a small graph is being described, in RDFa-syntax using a schema.org vocabulary and a Wikidata ID:
<div vocab="https://schema.org/" typeof="Person">
<span property="name">Paul Schuster</span> was born in
<span property="birthPlace" typeof="Place" href="https://www.wikidata.org/entity/Q1731">
<span property="name">Dresden</span>.
</span>
</div>

The example defines the following five triples (shown in Turtle syntax). Each triple represents one edge in the resulting graph: the first element of the triple (the subject) is the name of the node where the edge starts, the second element (the predicate) the type of the edge, and the last and third element (the object) either the name of the node where the edge ends or a literal value (e.g. a text, a number, etc.).
_:a <https://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#type> <https://schema.org/Person> .
_:a <https://schema.org/name> "Paul Schuster" .
_:a <https://schema.org/birthPlace> <https://www.wikidata.org/entity/Q1731> .
<https://www.wikidata.org/entity/Q1731> <https://schema.org/itemtype> <https://schema.org/Place> .
<https://www.wikidata.org/entity/Q1731> <https://schema.org/name> "Dresden" .
The triples result in the graph shown in the given figure.
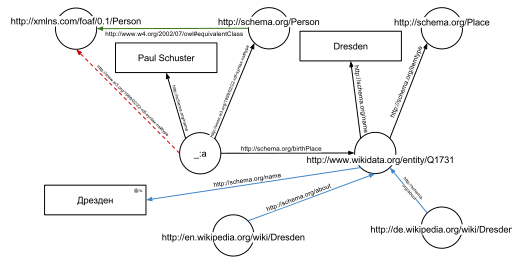
One of the advantages of using Uniform Resource Identifiers (URIs) is that they can be dereferenced using the HTTP protocol. According to the so-called Linked Open Data principles, such a dereferenced URI should result in a document that offers further data about the given URI. In this example, all URIs, both for edges and nodes (e.g. http://schema.org/Person, http://schema.org/birthPlace, http://www.wikidata.org/entity/Q1731) can be dereferenced and will result in further RDF graphs, describing the URI, e.g. that Dresden is a city in Germany, or that a person, in the sense of that URI, can be fictional.
The second graph shows the previous example, but now enriched with a few of the triples from the documents that result from dereferencing https://schema.org/Person (green edge) and https://www.wikidata.org/entity/Q1731 (blue edges).
Additionally to the edges given in the involved documents explicitly, edges can be automatically inferred: the triple
_:a <https://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#type> <http://schema.org/Person> .
from the original RDFa fragment and the triple
<https://schema.org/Person> <http://www.w3.org/2002/07/owl#equivalentClass> <http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/Person> .
from the document at https://schema.org/Person (green edge in the figure) allow to infer the following triple, given OWL semantics (red dashed line in the second Figure):
_:a <https://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#type> <http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/Person> .
The concept of the semantic network model was formed in the early 1960s by researchers such as the cognitive scientist Allan M. Collins, linguist Ross Quillian and psychologist Elizabeth F. Loftus as a form to represent semantically structured knowledge. When applied in the context of the modern internet, it extends the network of hyperlinked human-readable web pages by inserting machine-readable metadata about pages and how they are related to each other. This enables automated agents to access the Web more intelligently and perform more tasks on behalf of users. The term "Semantic Web" was coined by Tim Berners-Lee,[7] the inventor of the World Wide Web and director of the World Wide Web Consortium ("W3C"), which oversees the development of proposed Semantic Web standards. He defines the Semantic Web as "a web of data that can be processed directly and indirectly by machines".
Many of the technologies proposed by the W3C already existed before they were positioned under the W3C umbrella. These are used in various contexts, particularly those dealing with information that encompasses a limited and defined domain, and where sharing data is a common necessity, such as scientific research or data exchange among businesses. In addition, other technologies with similar goals have emerged, such as microformats.
Many files on a typical computer can be loosely divided into either human-readable documents, or machine-readable data. Examples of human-readable document files are mail messages, reports, and brochures. Examples of machine-readable data files are calendars, address books, playlists, and spreadsheets, which are presented to a user using an application program that lets the files be viewed, searched, and combined.
Currently, the World Wide Web is based mainly on documents written in Hypertext Markup Language (HTML), a markup convention that is used for coding a body of text interspersed with multimedia objects such as images and interactive forms. Metadata tags provide a method by which computers can categorize the content of web pages. In the examples below, the field names "keywords", "description" and "author" are assigned values such as "computing", and "cheap widgets for sale" and "John Doe".
<meta name="keywords" content="computing, computer studies, computer" />
<meta name="description" content="Cheap widgets for sale" />
<meta name="author" content="John Doe" />
Because of this metadata tagging and categorization, other computer systems that want to access and share this data can easily identify the relevant values.
With HTML and a tool to render it (perhaps web browser software, perhaps another user agent), one can create and present a page that lists items for sale. The HTML of this catalog page can make simple, document-level assertions such as "this document's title is 'Widget Superstore'", but there is no capability within the HTML itself to assert unambiguously that, for example, item number X586172 is an Acme Gizmo with a retail price of €199, or that it is a consumer product. Rather, HTML can only say that the span of text "X586172" is something that should be positioned near "Acme Gizmo" and "€199", etc. There is no way to say "this is a catalog" or even to establish that "Acme Gizmo" is a kind of title or that "€199" is a price. There is also no way to express that these pieces of information are bound together in describing a discrete item, distinct from other items perhaps listed on the page.
Semantic HTML refers to the traditional HTML practice of markup following intention, rather than specifying layout details directly. For example, the use of <em> denoting "emphasis" rather than <i>, which specifies italics. Layout details are left up to the browser, in combination with Cascading Style Sheets. But this practice falls short of specifying the semantics of objects such as items for sale or prices.
Microformats extend HTML syntax to create machine-readable semantic markup about objects including people, organizations, events and products.[13] Similar initiatives include RDFa, Microdata and Schema.org.
The Semantic Web takes the solution further. It involves publishing in languages specifically designed for data: Resource Description Framework (RDF), Web Ontology Language (OWL), and Extensible Markup Language (XML). HTML describes documents and the links between them. RDF, OWL, and XML, by contrast, can describe arbitrary things such as people, meetings, or airplane parts.
These technologies are combined in order to provide descriptions that supplement or replace the content of Web documents. Thus, content may manifest itself as descriptive data stored in Web-accessible databases,[14] or as markup within documents (particularly, in Extensible HTML (XHTML) interspersed with XML, or, more often, purely in XML, with layout or rendering cues stored separately). The machine-readable descriptions enable content managers to add meaning to the content, i.e., to describe the structure of the knowledge we have about that content. In this way, a machine can process knowledge itself, instead of text, using processes similar to human deductive reasoning and inference, thereby obtaining more meaningful results and helping computers to perform automated information gathering and research.
An example of a tag that would be used in a non-semantic web page:
<item>blog</item>
Encoding similar information in a semantic web page might look like this:
<item rdf:about="https://example.org/semantic-web/">Semantic Web</item>
Tim Berners-Lee calls the resulting network of Linked Data the Giant Global Graph, in contrast to the HTML-based World Wide Web. Berners-Lee posits that if the past was document sharing, the future is data sharing. His answer to the question of "how" provides three points of instruction. One, a URL should point to the data. Two, anyone accessing the URL should get data back. Three, relationships in the data should point to additional URLs with data.
Tags, including hierarchical categories and tags that are collaboratively added and maintained (e.g. with folksonomies) can be considered part of, of potential use to or a step towards the semantic Web vision.[15][16][17]
Unique identifiers, including hierarchical categories and collaboratively added ones, analysis tools and metadata, including tags, can be used to create forms of semantic webs – webs that are to a certain degree semantic.[18] In particular, such has been used for structuring scientific research i.a. by research topics and scientific fields by the projects OpenAlex,[19][20][21] Wikidata and Scholia which are under development and provide APIs, Web-pages, feeds and graphs for various semantic queries.
Tim Berners-Lee has described the Semantic Web as a component of Web 3.0.[22]
People keep asking what Web 3.0 is. I think maybe when you've got an overlay of scalable vector graphics – everything rippling and folding and looking misty – on Web 2.0 and access to a semantic Web integrated across a huge space of data, you'll have access to an unbelievable data resource …
— Tim Berners-Lee, 2006
"Semantic Web" is sometimes used as a synonym for "Web 3.0",[23] though the definition of each term varies.
The next generation of the Web is often termed Web 4.0, but its definition is not clear. According to some sources, it is a Web that involves artificial intelligence,[24] the internet of things, pervasive computing, ubiquitous computing and the Web of Things among other concepts.[25] According to the European Union, Web 4.0 is "the expected fourth generation of the World Wide Web. Using advanced artificial and ambient intelligence, the internet of things, trusted blockchain transactions, virtual worlds and XR capabilities, digital and real objects and environments are fully integrated and communicate with each other, enabling truly intuitive, immersive experiences, seamlessly blending the physical and digital worlds".[26]
Some of the challenges for the Semantic Web include vastness, vagueness, uncertainty, inconsistency, and deceit. Automated reasoning systems will have to deal with all of these issues in order to deliver on the promise of the Semantic Web.
This list of challenges is illustrative rather than exhaustive, and it focuses on the challenges to the "unifying logic" and "proof" layers of the Semantic Web. The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) Incubator Group for Uncertainty Reasoning for the World Wide Web[27] (URW3-XG) final report lumps these problems together under the single heading of "uncertainty".[28] Many of the techniques mentioned here will require extensions to the Web Ontology Language (OWL) for example to annotate conditional probabilities. This is an area of active research.[29]
Standardization for Semantic Web in the context of Web 3.0 is under the care of W3C.[30]
The term "Semantic Web" is often used more specifically to refer to the formats and technologies that enable it.[5] The collection, structuring and recovery of linked data are enabled by technologies that provide a formal description of concepts, terms, and relationships within a given knowledge domain. These technologies are specified as W3C standards and include:
The Semantic Web Stack illustrates the architecture of the Semantic Web. The functions and relationships of the components can be summarized as follows:[31]
Well-established standards:
Not yet fully realized:
The intent is to enhance the usability and usefulness of the Web and its interconnected resources by creating semantic web services, such as:
<meta> tags used in today's Web pages to supply information for Web search engines using web crawlers). This could be machine-understandable information about the human-understandable content of the document (such as the creator, title, description, etc.) or it could be purely metadata representing a set of facts (such as resources and services elsewhere on the site). Note that anything that can be identified with a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) can be described, so the semantic web can reason about animals, people, places, ideas, etc. There are four semantic annotation formats that can be used in HTML documents; Microformat, RDFa, Microdata and JSON-LD.[35] Semantic markup is often generated automatically, rather than manually.
Such services could be useful to public search engines, or could be used for knowledge management within an organization. Business applications include:
In a corporation, there is a closed group of users and the management is able to enforce company guidelines like the adoption of specific ontologies and use of semantic annotation. Compared to the public Semantic Web there are lesser requirements on scalability and the information circulating within a company can be more trusted in general; privacy is less of an issue outside of handling of customer data.
Critics question the basic feasibility of a complete or even partial fulfillment of the Semantic Web, pointing out both difficulties in setting it up and a lack of general-purpose usefulness that prevents the required effort from being invested. In a 2003 paper, Marshall and Shipman point out the cognitive overhead inherent in formalizing knowledge, compared to the authoring of traditional web hypertext:[46]
While learning the basics of HTML is relatively straightforward, learning a knowledge representation language or tool requires the author to learn about the representation's methods of abstraction and their effect on reasoning. For example, understanding the class-instance relationship, or the superclass-subclass relationship, is more than understanding that one concept is a "type of" another concept. [...] These abstractions are taught to computer scientists generally and knowledge engineers specifically but do not match the similar natural language meaning of being a "type of" something. Effective use of such a formal representation requires the author to become a skilled knowledge engineer in addition to any other skills required by the domain. [...] Once one has learned a formal representation language, it is still often much more effort to express ideas in that representation than in a less formal representation [...]. Indeed, this is a form of programming based on the declaration of semantic data and requires an understanding of how reasoning algorithms will interpret the authored structures.
According to Marshall and Shipman, the tacit and changing nature of much knowledge adds to the knowledge engineering problem, and limits the Semantic Web's applicability to specific domains. A further issue that they point out are domain- or organization-specific ways to express knowledge, which must be solved through community agreement rather than only technical means.[46] As it turns out, specialized communities and organizations for intra-company projects have tended to adopt semantic web technologies greater than peripheral and less-specialized communities.[47] The practical constraints toward adoption have appeared less challenging where domain and scope is more limited than that of the general public and the World-Wide Web.[47]
Finally, Marshall and Shipman see pragmatic problems in the idea of (Knowledge Navigator-style) intelligent agents working in the largely manually curated Semantic Web:[46]
In situations in which user needs are known and distributed information resources are well described, this approach can be highly effective; in situations that are not foreseen and that bring together an unanticipated array of information resources, the Google approach is more robust. Furthermore, the Semantic Web relies on inference chains that are more brittle; a missing element of the chain results in a failure to perform the desired action, while the human can supply missing pieces in a more Google-like approach. [...] cost-benefit tradeoffs can work in favor of specially-created Semantic Web metadata directed at weaving together sensible well-structured domain-specific information resources; close attention to user/customer needs will drive these federations if they are to be successful.
Cory Doctorow's critique ("metacrap")[48] is from the perspective of human behavior and personal preferences. For example, people may include spurious metadata into Web pages in an attempt to mislead Semantic Web engines that naively assume the metadata's veracity. This phenomenon was well known with metatags that fooled the Altavista ranking algorithm into elevating the ranking of certain Web pages: the Google indexing engine specifically looks for such attempts at manipulation. Peter Gärdenfors and Timo Honkela point out that logic-based semantic web technologies cover only a fraction of the relevant phenomena related to semantics.[49][50]
Enthusiasm about the semantic web could be tempered by concerns regarding censorship and privacy. For instance, text-analyzing techniques can now be easily bypassed by using other words, metaphors for instance, or by using images in place of words. An advanced implementation of the semantic web would make it much easier for governments to control the viewing and creation of online information, as this information would be much easier for an automated content-blocking machine to understand. In addition, the issue has also been raised that, with the use of FOAF files and geolocation meta-data, there would be very little anonymity associated with the authorship of articles on things such as a personal blog. Some of these concerns were addressed in the "Policy Aware Web" project[51] and is an active research and development topic.
Another criticism of the semantic web is that it would be much more time-consuming to create and publish content because there would need to be two formats for one piece of data: one for human viewing and one for machines. However, many web applications in development are addressing this issue by creating a machine-readable format upon the publishing of data or the request of a machine for such data. The development of microformats has been one reaction to this kind of criticism. Another argument in defense of the feasibility of semantic web is the likely falling price of human intelligence tasks in digital labor markets, such as Amazon's Mechanical Turk.[citation needed]
Specifications such as eRDF and RDFa allow arbitrary RDF data to be embedded in HTML pages. The GRDDL (Gleaning Resource Descriptions from Dialects of Language) mechanism allows existing material (including microformats) to be automatically interpreted as RDF, so publishers only need to use a single format, such as HTML.
The first research group explicitly focusing on the Corporate Semantic Web was the ACACIA team at INRIA-Sophia-Antipolis, founded in 2002. Results of their work include the RDF(S) based Corese[52] search engine, and the application of semantic web technology in the realm of distributed artificial intelligence for knowledge management (e.g. ontologies and multi-agent systems for corporate semantic Web) [53] and E-learning.[54]
Since 2008, the Corporate Semantic Web research group, located at the Free University of Berlin, focuses on building blocks: Corporate Semantic Search, Corporate Semantic Collaboration, and Corporate Ontology Engineering.[55]
Ontology engineering research includes the question of how to involve non-expert users in creating ontologies and semantically annotated content[56] and for extracting explicit knowledge from the interaction of users within enterprises.
Tim O'Reilly, who coined the term Web 2.0, proposed a long-term vision of the Semantic Web as a web of data, where sophisticated applications are navigating and manipulating it.[57] The data web transforms the World Wide Web from a distributed file system into a distributed database.[58]
cite journal: Cite journal requires |journal= (help)cite book: |work= ignored (help)
|
|
This article needs to be updated. (December 2024)
|
|
|
This article is written like a personal reflection, personal essay, or argumentative essay that states a Wikipedia editor's personal feelings or presents an original argument about a topic. (January 2025)
|
|
|
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
| Part of a series on |
| Internet marketing |
|---|
| Search engine marketing |
| Display advertising |
| Affiliate marketing |
| Mobile advertising |
Search engine optimization (SEO) is the process of improving the quality and quantity of website traffic to a website or a web page from search engines.[1][2] SEO targets unpaid search traffic (usually referred to as "organic" results) rather than direct traffic, referral traffic, social media traffic, or paid traffic.
Unpaid search engine traffic may originate from a variety of kinds of searches, including image search, video search, academic search,[3] news search, and industry-specific vertical search engines.
As an Internet marketing strategy, SEO considers how search engines work, the computer-programmed algorithms that dictate search engine results, what people search for, the actual search queries or keywords typed into search engines, and which search engines are preferred by a target audience. SEO is performed because a website will receive more visitors from a search engine when websites rank higher within a search engine results page (SERP), with the aim of either converting the visitors or building brand awareness.[4]
Webmasters and content providers began optimizing websites for search engines in the mid-1990s, as the first search engines were cataloging the early Web. Initially, webmasters submitted the address of a page, or URL to the various search engines, which would send a web crawler to crawl that page, extract links to other pages from it, and return information found on the page to be indexed.[5]
According to a 2004 article by former industry analyst and current Google employee Danny Sullivan, the phrase "search engine optimization" probably came into use in 1997. Sullivan credits SEO practitioner Bruce Clay as one of the first people to popularize the term.[6]
Early versions of search algorithms relied on webmaster-provided information such as the keyword meta tag or index files in engines like ALIWEB. Meta tags provide a guide to each page's content. Using metadata to index pages was found to be less than reliable, however, because the webmaster's choice of keywords in the meta tag could potentially be an inaccurate representation of the site's actual content. Flawed data in meta tags, such as those that were inaccurate or incomplete, created the potential for pages to be mischaracterized in irrelevant searches.[7][dubious – discuss] Web content providers also manipulated attributes within the HTML source of a page in an attempt to rank well in search engines.[8] By 1997, search engine designers recognized that webmasters were making efforts to rank in search engines and that some webmasters were manipulating their rankings in search results by stuffing pages with excessive or irrelevant keywords. Early search engines, such as Altavista and Infoseek, adjusted their algorithms to prevent webmasters from manipulating rankings.[9]
By heavily relying on factors such as keyword density, which were exclusively within a webmaster's control, early search engines suffered from abuse and ranking manipulation. To provide better results to their users, search engines had to adapt to ensure their results pages showed the most relevant search results, rather than unrelated pages stuffed with numerous keywords by unscrupulous webmasters. This meant moving away from heavy reliance on term density to a more holistic process for scoring semantic signals.[10]
Search engines responded by developing more complex ranking algorithms, taking into account additional factors that were more difficult for webmasters to manipulate.[citation needed]
Some search engines have also reached out to the SEO industry and are frequent sponsors and guests at SEO conferences, webchats, and seminars. Major search engines provide information and guidelines to help with website optimization.[11][12] Google has a Sitemaps program to help webmasters learn if Google is having any problems indexing their website and also provides data on Google traffic to the website.[13] Bing Webmaster Tools provides a way for webmasters to submit a sitemap and web feeds, allows users to determine the "crawl rate", and track the web pages index status.
In 2015, it was reported that Google was developing and promoting mobile search as a key feature within future products. In response, many brands began to take a different approach to their Internet marketing strategies.[14]
In 1998, two graduate students at Stanford University, Larry Page and Sergey Brin, developed "Backrub", a search engine that relied on a mathematical algorithm to rate the prominence of web pages. The number calculated by the algorithm, PageRank, is a function of the quantity and strength of inbound links.[15] PageRank estimates the likelihood that a given page will be reached by a web user who randomly surfs the web and follows links from one page to another. In effect, this means that some links are stronger than others, as a higher PageRank page is more likely to be reached by the random web surfer.
Page and Brin founded Google in 1998.[16] Google attracted a loyal following among the growing number of Internet users, who liked its simple design.[17] Off-page factors (such as PageRank and hyperlink analysis) were considered as well as on-page factors (such as keyword frequency, meta tags, headings, links and site structure) to enable Google to avoid the kind of manipulation seen in search engines that only considered on-page factors for their rankings. Although PageRank was more difficult to game, webmasters had already developed link-building tools and schemes to influence the Inktomi search engine, and these methods proved similarly applicable to gaming PageRank. Many sites focus on exchanging, buying, and selling links, often on a massive scale. Some of these schemes involved the creation of thousands of sites for the sole purpose of link spamming.[18]
By 2004, search engines had incorporated a wide range of undisclosed factors in their ranking algorithms to reduce the impact of link manipulation.[19] The leading search engines, Google, Bing, and Yahoo, do not disclose the algorithms they use to rank pages. Some SEO practitioners have studied different approaches to search engine optimization and have shared their personal opinions.[20] Patents related to search engines can provide information to better understand search engines.[21] In 2005, Google began personalizing search results for each user. Depending on their history of previous searches, Google crafted results for logged in users.[22]
In 2007, Google announced a campaign against paid links that transfer PageRank.[23] On June 15, 2009, Google disclosed that they had taken measures to mitigate the effects of PageRank sculpting by use of the nofollow attribute on links. Matt Cutts, a well-known software engineer at Google, announced that Google Bot would no longer treat any no follow links, in the same way, to prevent SEO service providers from using nofollow for PageRank sculpting.[24] As a result of this change, the usage of nofollow led to evaporation of PageRank. In order to avoid the above, SEO engineers developed alternative techniques that replace nofollowed tags with obfuscated JavaScript and thus permit PageRank sculpting. Additionally, several solutions have been suggested that include the usage of iframes, Flash, and JavaScript.[25]
In December 2009, Google announced it would be using the web search history of all its users in order to populate search results.[26] On June 8, 2010 a new web indexing system called Google Caffeine was announced. Designed to allow users to find news results, forum posts, and other content much sooner after publishing than before, Google Caffeine was a change to the way Google updated its index in order to make things show up quicker on Google than before. According to Carrie Grimes, the software engineer who announced Caffeine for Google, "Caffeine provides 50 percent fresher results for web searches than our last index..."[27] Google Instant, real-time-search, was introduced in late 2010 in an attempt to make search results more timely and relevant. Historically site administrators have spent months or even years optimizing a website to increase search rankings. With the growth in popularity of social media sites and blogs, the leading engines made changes to their algorithms to allow fresh content to rank quickly within the search results.[28]
In February 2011, Google announced the Panda update, which penalizes websites containing content duplicated from other websites and sources. Historically websites have copied content from one another and benefited in search engine rankings by engaging in this practice. However, Google implemented a new system that punishes sites whose content is not unique.[29] The 2012 Google Penguin attempted to penalize websites that used manipulative techniques to improve their rankings on the search engine.[30] Although Google Penguin has been presented as an algorithm aimed at fighting web spam, it really focuses on spammy links[31] by gauging the quality of the sites the links are coming from. The 2013 Google Hummingbird update featured an algorithm change designed to improve Google's natural language processing and semantic understanding of web pages. Hummingbird's language processing system falls under the newly recognized term of "conversational search", where the system pays more attention to each word in the query in order to better match the pages to the meaning of the query rather than a few words.[32] With regards to the changes made to search engine optimization, for content publishers and writers, Hummingbird is intended to resolve issues by getting rid of irrelevant content and spam, allowing Google to produce high-quality content and rely on them to be 'trusted' authors.
In October 2019, Google announced they would start applying BERT models for English language search queries in the US. Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) was another attempt by Google to improve their natural language processing, but this time in order to better understand the search queries of their users.[33] In terms of search engine optimization, BERT intended to connect users more easily to relevant content and increase the quality of traffic coming to websites that are ranking in the Search Engine Results Page.

The leading search engines, such as Google, Bing, and Yahoo!, use crawlers to find pages for their algorithmic search results. Pages that are linked from other search engine-indexed pages do not need to be submitted because they are found automatically. The Yahoo! Directory and DMOZ, two major directories which closed in 2014 and 2017 respectively, both required manual submission and human editorial review.[34] Google offers Google Search Console, for which an XML Sitemap feed can be created and submitted for free to ensure that all pages are found, especially pages that are not discoverable by automatically following links[35] in addition to their URL submission console.[36] Yahoo! formerly operated a paid submission service that guaranteed to crawl for a cost per click;[37] however, this practice was discontinued in 2009.
Search engine crawlers may look at a number of different factors when crawling a site. Not every page is indexed by search engines. The distance of pages from the root directory of a site may also be a factor in whether or not pages get crawled.[38]
Mobile devices are used for the majority of Google searches.[39] In November 2016, Google announced a major change to the way they are crawling websites and started to make their index mobile-first, which means the mobile version of a given website becomes the starting point for what Google includes in their index.[40] In May 2019, Google updated the rendering engine of their crawler to be the latest version of Chromium (74 at the time of the announcement). Google indicated that they would regularly update the Chromium rendering engine to the latest version.[41] In December 2019, Google began updating the User-Agent string of their crawler to reflect the latest Chrome version used by their rendering service. The delay was to allow webmasters time to update their code that responded to particular bot User-Agent strings. Google ran evaluations and felt confident the impact would be minor.[42]
To avoid undesirable content in the search indexes, webmasters can instruct spiders not to crawl certain files or directories through the standard robots.txt file in the root directory of the domain. Additionally, a page can be explicitly excluded from a search engine's database by using a meta tag specific to robots (usually <meta name="robots" content="noindex"> ). When a search engine visits a site, the robots.txt located in the root directory is the first file crawled. The robots.txt file is then parsed and will instruct the robot as to which pages are not to be crawled. As a search engine crawler may keep a cached copy of this file, it may on occasion crawl pages a webmaster does not wish to crawl. Pages typically prevented from being crawled include login-specific pages such as shopping carts and user-specific content such as search results from internal searches. In March 2007, Google warned webmasters that they should prevent indexing of internal search results because those pages are considered search spam.[43]
In 2020, Google sunsetted the standard (and open-sourced their code) and now treats it as a hint rather than a directive. To adequately ensure that pages are not indexed, a page-level robot's meta tag should be included.[44]
A variety of methods can increase the prominence of a webpage within the search results. Cross linking between pages of the same website to provide more links to important pages may improve its visibility. Page design makes users trust a site and want to stay once they find it. When people bounce off a site, it counts against the site and affects its credibility.[45]
Writing content that includes frequently searched keyword phrases so as to be relevant to a wide variety of search queries will tend to increase traffic. Updating content so as to keep search engines crawling back frequently can give additional weight to a site. Adding relevant keywords to a web page's metadata, including the title tag and meta description, will tend to improve the relevancy of a site's search listings, thus increasing traffic. URL canonicalization of web pages accessible via multiple URLs, using the canonical link element[46] or via 301 redirects can help make sure links to different versions of the URL all count towards the page's link popularity score. These are known as incoming links, which point to the URL and can count towards the page link's popularity score, impacting the credibility of a website.[45]

SEO techniques can be classified into two broad categories: techniques that search engine companies recommend as part of good design ("white hat"), and those techniques of which search engines do not approve ("black hat"). Search engines attempt to minimize the effect of the latter, among them spamdexing. Industry commentators have classified these methods and the practitioners who employ them as either white hat SEO or black hat SEO.[47] White hats tend to produce results that last a long time, whereas black hats anticipate that their sites may eventually be banned either temporarily or permanently once the search engines discover what they are doing.[48]
An SEO technique is considered a white hat if it conforms to the search engines' guidelines and involves no deception. As the search engine guidelines[11][12][49] are not written as a series of rules or commandments, this is an important distinction to note. White hat SEO is not just about following guidelines but is about ensuring that the content a search engine indexes and subsequently ranks is the same content a user will see. White hat advice is generally summed up as creating content for users, not for search engines, and then making that content easily accessible to the online "spider" algorithms, rather than attempting to trick the algorithm from its intended purpose. White hat SEO is in many ways similar to web development that promotes accessibility,[50] although the two are not identical.
Black hat SEO attempts to improve rankings in ways that are disapproved of by the search engines or involve deception. One black hat technique uses hidden text, either as text colored similar to the background, in an invisible div, or positioned off-screen. Another method gives a different page depending on whether the page is being requested by a human visitor or a search engine, a technique known as cloaking. Another category sometimes used is grey hat SEO. This is in between the black hat and white hat approaches, where the methods employed avoid the site being penalized but do not act in producing the best content for users. Grey hat SEO is entirely focused on improving search engine rankings.
Search engines may penalize sites they discover using black or grey hat methods, either by reducing their rankings or eliminating their listings from their databases altogether. Such penalties can be applied either automatically by the search engines' algorithms or by a manual site review. One example was the February 2006 Google removal of both BMW Germany and Ricoh Germany for the use of deceptive practices.[51] Both companies subsequently apologized, fixed the offending pages, and were restored to Google's search engine results page.[52]
Companies that employ black hat techniques or other spammy tactics can get their client websites banned from the search results. In 2005, the Wall Street Journal reported on a company, Traffic Power, which allegedly used high-risk techniques and failed to disclose those risks to its clients.[53] Wired magazine reported that the same company sued blogger and SEO Aaron Wall for writing about the ban.[54] Google's Matt Cutts later confirmed that Google had banned Traffic Power and some of its clients.[55]
SEO is not an appropriate strategy for every website, and other Internet marketing strategies can be more effective, such as paid advertising through pay-per-click (PPC) campaigns, depending on the site operator's goals.[editorializing] Search engine marketing (SEM) is the practice of designing, running, and optimizing search engine ad campaigns. Its difference from SEO is most simply depicted as the difference between paid and unpaid priority ranking in search results. SEM focuses on prominence more so than relevance; website developers should regard SEM with the utmost importance with consideration to visibility as most navigate to the primary listings of their search.[56] A successful Internet marketing campaign may also depend upon building high-quality web pages to engage and persuade internet users, setting up analytics programs to enable site owners to measure results, and improving a site's conversion rate.[57][58] In November 2015, Google released a full 160-page version of its Search Quality Rating Guidelines to the public,[59] which revealed a shift in their focus towards "usefulness" and mobile local search. In recent years the mobile market has exploded, overtaking the use of desktops, as shown in by StatCounter in October 2016, where they analyzed 2.5 million websites and found that 51.3% of the pages were loaded by a mobile device.[60] Google has been one of the companies that are utilizing the popularity of mobile usage by encouraging websites to use their Google Search Console, the Mobile-Friendly Test, which allows companies to measure up their website to the search engine results and determine how user-friendly their websites are. The closer the keywords are together their ranking will improve based on key terms.[45]
SEO may generate an adequate return on investment. However, search engines are not paid for organic search traffic, their algorithms change, and there are no guarantees of continued referrals. Due to this lack of guarantee and uncertainty, a business that relies heavily on search engine traffic can suffer major losses if the search engines stop sending visitors.[61] Search engines can change their algorithms, impacting a website's search engine ranking, possibly resulting in a serious loss of traffic. According to Google's CEO, Eric Schmidt, in 2010, Google made over 500 algorithm changes – almost 1.5 per day.[62] It is considered a wise business practice for website operators to liberate themselves from dependence on search engine traffic.[63] In addition to accessibility in terms of web crawlers (addressed above), user web accessibility has become increasingly important for SEO.
Optimization techniques are highly tuned to the dominant search engines in the target market. The search engines' market shares vary from market to market, as does competition. In 2003, Danny Sullivan stated that Google represented about 75% of all searches.[64] In markets outside the United States, Google's share is often larger, and data showed Google was the dominant search engine worldwide as of 2007.[65] As of 2006, Google had an 85–90% market share in Germany.[66] While there were hundreds of SEO firms in the US at that time, there were only about five in Germany.[66] As of March 2024, Google still had a significant market share of 89.85% in Germany.[67] As of June 2008, the market share of Google in the UK was close to 90% according to Hitwise.[68][obsolete source] As of March 2024, Google's market share in the UK was 93.61%.[69]
Successful search engine optimization (SEO) for international markets requires more than just translating web pages. It may also involve registering a domain name with a country-code top-level domain (ccTLD) or a relevant top-level domain (TLD) for the target market, choosing web hosting with a local IP address or server, and using a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to improve website speed and performance globally. It is also important to understand the local culture so that the content feels relevant to the audience. This includes conducting keyword research for each market, using hreflang tags to target the right languages, and building local backlinks. However, the core SEO principles—such as creating high-quality content, improving user experience, and building links—remain the same, regardless of language or region.[66]
Regional search engines have a strong presence in specific markets:
By the early 2000s, businesses recognized that the web and search engines could help them reach global audiences. As a result, the need for multilingual SEO emerged.[74] In the early years of international SEO development, simple translation was seen as sufficient. However, over time, it became clear that localization and transcreation—adapting content to local language, culture, and emotional resonance—were far more effective than basic translation.[75]
On October 17, 2002, SearchKing filed suit in the United States District Court, Western District of Oklahoma, against the search engine Google. SearchKing's claim was that Google's tactics to prevent spamdexing constituted a tortious interference with contractual relations. On May 27, 2003, the court granted Google's motion to dismiss the complaint because SearchKing "failed to state a claim upon which relief may be granted."[76][77]
In March 2006, KinderStart filed a lawsuit against Google over search engine rankings. KinderStart's website was removed from Google's index prior to the lawsuit, and the amount of traffic to the site dropped by 70%. On March 16, 2007, the United States District Court for the Northern District of California (San Jose Division) dismissed KinderStart's complaint without leave to amend and partially granted Google's motion for Rule 11 sanctions against KinderStart's attorney, requiring him to pay part of Google's legal expenses.[78][79]
Parramatta (/ËŒpærəˈmætÉ™/; Dharuk: Burramatta) is a suburb and major commercial centre in Greater Western Sydney.[7][8] Parramatta is located approximately 24 kilometres (15 mi) west of the Sydney CBD, on the banks of the Parramatta River.[2] It is commonly regarded as the secondary central business district of metropolitan Sydney.
Parramatta is the municipal seat of the local government area of the City of Parramatta and is often regarded as one of the primary centres of the Greater Sydney metropolitan region, along with the Sydney CBD, Penrith, Campbelltown, and Liverpool.[9] Parramatta also has a long history as a second administrative centre in the Sydney metropolitan region, playing host to a number of government departments,[10] as well as state and federal courts. It is often colloquially referred to as "Parra".
Parramatta, which was founded as a British settlement in 1788, the same year as Sydney, is the oldest inland European settlement in Australia and serves as the economic centre of Greater Western Sydney.[11] Since 2000, state government agencies such as the New South Wales Police Force and Sydney Water[12] have relocated to Parramatta from Central Sydney. The 151st meridian east runs directly through the suburb.
Radiocarbon dating suggests human activity occurred in Parramatta from around 30,000 years ago.[13] The Darug people who lived in the area before European settlement regarded the area as rich in food from the river and forests. They named the area Baramada or Burramatta ('Parramatta') which means Eel ("Burra") Place ("matta"), with the resident Indigenous people being called the Burramattagal. Similar Darug words include Cabramatta (Grub place) and Wianamatta (Mother place).[14] Other references[which?] are derived from the words of Captain Watkin Tench, a white British man with a poor understanding of the Darug language, and are incorrect.[citation needed] To this day many eels and other sea creatures are attracted to nutrients that are concentrated where the saltwater of Port Jackson meets the freshwater of the Parramatta River. The Parramatta Eels rugby league club chose their symbol as a result of this phenomenon.



Parramatta was colonised by the British in 1788, the same year as Sydney. As such, Parramatta is the second oldest city in Australia, being only 10 months younger than Sydney. The British colonists, who had arrived in January 1788 on the First Fleet at Sydney Cove, had only enough food to support themselves for a short time and the soil around Sydney Cove proved too poor to grow the amount of food that 1,000 convicts, soldiers and administrators needed to survive. During 1788, Governor Arthur Phillip had reconnoitred several places before choosing Parramatta as the most likely place for a successful large farm.[15] Parramatta was the furthest navigable point inland on the Parramatta River (i.e. furthest from the thin, sandy coastal soil) and also the point at which the river became freshwater and therefore useful for farming.
On Sunday 2 November 1788, Governor Phillip took a detachment of marines along with a surveyor and, in boats, made his way upriver to a location that he called The Crescent, a defensible hill curved round a river bend, now in Parramatta Park. The Burramattagal were rapidly displaced with notable residents Maugoran, Boorong and Baludarri being forced from their lands.[16]
As a settlement developed, Governor Phillip gave it the name "Rose Hill" after British politician George Rose.[17] On 4 June 1791 Phillip changed the name of the township to Parramatta, approximating the term used by the local Aboriginal people.[18] A neighbouring suburb acquired the name "Rose Hill", which today is spelt "Rosehill".

In an attempt to deal with the food crisis, Phillip in 1789 granted a convict named James Ruse the land of Experiment Farm at Parramatta on the condition that he develop a viable agriculture. There, Ruse became the first European to successfully grow grain in Australia. The Parramatta area was also the site of the pioneering of the Australian wool industry by John Macarthur's Elizabeth Farm in the 1790s. Philip Gidley King's account of his visit to Parramatta on 9 April 1790 is one of the earliest descriptions of the area. Walking four miles with Governor Phillip to Prospect, he saw undulating grassland interspersed with magnificent trees and a great number of kangaroos and emus.[19]
The Battle of Parramatta, a major battle of the Australian frontier wars, occurred in March 1797 where Eora leader Pemulwuy led a group of Bidjigal warriors, estimated to be at least 100, in an attack on the town of Parramatta. The local garrison withdrew to their barracks and Pemulwuy held the town until he was eventually shot and wounded. A year later, a government farm at Toongabbie was attacked by Pemulwuy, who challenged the New South Wales Corps to a fight.[20][21]
Governor Arthur Phillip built a small house for himself on the hill of The Crescent. In 1799 this was replaced by a larger residence which, substantially improved by Governor Lachlan Macquarie from 1815 to 1818, has survived to the present day, making it the oldest surviving Government House anywhere in Australia. It was used as a retreat by Governors until the 1850s, with one Governor (Governor Brisbane) making it his principal home for a short period in the 1820s.
In 1803, another famous incident occurred in Parramatta, involving a convicted criminal named Joseph Samuel, originally from England. Samuel was convicted of murder and sentenced to death by hanging, but the rope broke. In the second attempt, the noose slipped off his neck. In the third attempt, the new rope broke. Governor King was summoned and pardoned Samuel, as the incident appeared to him to be divine intervention.[22]
In 1814, Macquarie opened a school for Aboriginal children at Parramatta as part of a policy of improving relations between Aboriginal and European communities. This school was later relocated to "Black Town".[23]
Parramatta was gazetted as a city on 19 November 1976, and later, a suburb on 10 June 1994.
The first significant skyscrapers began to emerge in Parramatta in the late 1990s and the suburb transformed into a major business and residential hub in the early 2000s. Since then, the suburb's growth has accelerated in the past decade.
On 20 December 2024, the first stage of the Parramatta Light Rail was completed.
Parramatta has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification: Cfa) with mild to cool, somewhat short winters and warm to usually hot summers, alongside moderate rainfall spread throughout the year.
Summer maximum temperatures are quite variable, often reaching above 35 °C (95 °F), on average 13.1 days in the summer season, and sometimes remaining in the low 20s, especially after a cold front or a sea breeze, such as the southerly buster. Northwesterlies can occasionally bring hot winds from the desert that can raise temperatures higher than 40 °C (104 °F) mostly from November to February, and sometimes above 44 °C (111 °F) in January severe heatwaves. The record highest temperature (since 1967) was 47.0 °C (116.6 °F) on 4 January 2020. Parramatta is warmer than Sydney CBD in the summer due to the urban heat island effect and its inland location. In extreme cases though, it can be 5–10 °C (9–18 °F) warmer than Sydney, especially when sea breezes do not penetrate inland on hot summer and spring days. For example, on 28 November 2009, the city reached 29.3 °C (84.7 °F),[24] while Parramatta reached 39.0 °C (102.2 °F),[25] almost 10 °C (18 °F) higher. In the summer, Parramatta, among other places in western Sydney, can often be the hottest place in the world because of the Blue Mountains trapping hot air in the region, in addition to the UHI effect.[26]
Rainfall is slightly higher during the first three months of the year because the anticlockwise-rotating subtropical high is to the south of the country, thereby allowing moist easterlies from the Tasman Sea to penetrate the city.[27][28] The second half of the year tends to be drier (late winter/spring) since the subtropical high is to the north of the city, thus permitting dry westerlies from the interior to dominate.[29] Drier winters are also owed to its position on the leeward side of the Great Dividing Range, which block westerly cold fronts (that are more common in late winter) and thus would become foehn winds, whereby allowing decent amount of sunny days and relatively low precipitation in that period.[30] Thunderstorms are common in the months from early spring to early autumn, occasionally quite severe thunderstorms can occur. Snow is virtually unknown, having been recorded only in 1836 and 1896[31] Parrammatta gets 106.6 days of clear skies annually.
Depending on the wind direction, summer weather may be humid or dry, though the humidity is mostly in the comfortable range, with the late summer/autumn period having a higher average humidity than late winter/early spring.
| Climate data for Parramatta North (1991–2020 averages, 1967–present extremes) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 47.0 (116.6) |
44.5 (112.1) |
40.5 (104.9) |
37.0 (98.6) |
29.2 (84.6) |
25.5 (77.9) |
26.8 (80.2) |
30.6 (87.1) |
36.5 (97.7) |
40.1 (104.2) |
42.7 (108.9) |
44.0 (111.2) |
47.0 (116.6) |
| Mean maximum °C (°F) | 40.1 (104.2) |
37.5 (99.5) |
33.9 (93.0) |
30.3 (86.5) |
26.2 (79.2) |
22.3 (72.1) |
22.7 (72.9) |
25.7 (78.3) |
30.8 (87.4) |
34.3 (93.7) |
36.6 (97.9) |
37.6 (99.7) |
41.6 (106.9) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 29.1 (84.4) |
28.3 (82.9) |
26.5 (79.7) |
23.9 (75.0) |
20.9 (69.6) |
18.2 (64.8) |
17.8 (64.0) |
19.5 (67.1) |
22.3 (72.1) |
24.5 (76.1) |
25.8 (78.4) |
27.7 (81.9) |
23.7 (74.7) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 17.9 (64.2) |
17.7 (63.9) |
15.9 (60.6) |
12.6 (54.7) |
9.6 (49.3) |
7.5 (45.5) |
6.3 (43.3) |
6.9 (44.4) |
9.4 (48.9) |
12.0 (53.6) |
14.3 (57.7) |
16.4 (61.5) |
12.2 (54.0) |
| Mean minimum °C (°F) | 12.9 (55.2) |
12.7 (54.9) |
10.9 (51.6) |
7.8 (46.0) |
4.5 (40.1) |
2.9 (37.2) |
1.7 (35.1) |
2.4 (36.3) |
4.5 (40.1) |
6.5 (43.7) |
8.6 (47.5) |
10.9 (51.6) |
1.2 (34.2) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 10.1 (50.2) |
9.2 (48.6) |
6.8 (44.2) |
4.0 (39.2) |
1.4 (34.5) |
0.8 (33.4) |
−1.0 (30.2) |
0.7 (33.3) |
0.7 (33.3) |
3.6 (38.5) |
4.0 (39.2) |
7.7 (45.9) |
−1.0 (30.2) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 89.9 (3.54) |
130.3 (5.13) |
99.1 (3.90) |
78.3 (3.08) |
61.3 (2.41) |
99.0 (3.90) |
48.0 (1.89) |
47.4 (1.87) |
48.5 (1.91) |
61.3 (2.41) |
82.0 (3.23) |
78.5 (3.09) |
923.6 (36.36) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1 mm) | 8.6 | 9.0 | 9.9 | 7.0 | 6.3 | 7.9 | 6.0 | 4.8 | 5.7 | 7.0 | 8.7 | 8.3 | 89.2 |
| Average afternoon relative humidity (%) | 56 | 59 | 58 | 56 | 59 | 58 | 55 | 45 | 46 | 50 | 54 | 55 | 54 |
| Average dew point °C (°F) | 16.2 (61.2) |
16.8 (62.2) |
15.5 (59.9) |
12.7 (54.9) |
9.9 (49.8) |
7.6 (45.7) |
5.6 (42.1) |
5.5 (41.9) |
7.7 (45.9) |
9.9 (49.8) |
12.3 (54.1) |
14.3 (57.7) |
11.2 (52.2) |
| Source: Bureau of Meteorology[32] | |||||||||||||

Church Street is home to many shops and restaurants. The northern end of Church Street, close to Lennox Bridge, features al fresco dining with a diverse range of cuisines. Immediately south of the CBD Church Street is known across Sydney as 'Auto Alley' for the many car dealerships lining both sides of the street as far as the M4 Motorway.[33]

Since 2000, Parramatta has seen the consolidation of its role as a government centre, with the relocation of agencies such as the New South Wales Police Force Headquarters and the Sydney Water Corporation[12] from Sydney CBD. At the same time, major construction work occurred around the railway station with the expansion of Westfield Shoppingtown and the creation of a new transport interchange. The western part of the Parramatta CBD is known as the Parramatta Justice Precinct and houses the corporate headquarters of the Department of Communities and Justice. Other legal offices include the Children's Court of New South Wales and the Sydney West Trial Courts, Legal Aid Commission of NSW, Office of Trustee and Guardian (formerly the Office of the Protective Commissioner), NSW Registry of Births, Deaths and Marriages, and the Office of the Director of Public Prosecutions. Nearby on Marsden Street is the Parramatta Courthouse and the Drug Court of New South Wales. The Garfield Barwick Commonwealth Law Courts Building (named in honour of Sir Garfield Barwick), houses courts of the Federal Magistrates Court and the Family Court of Australia. The NSW Government has also announced plans to secure up to 45,000 m2 of new A-grade leased office space in Parramatta to relocate a further 4,000 workers from the Sydney CBD.[34]

Parramatta Square (previously known as Civic Place) is a civic precinct located in the heart of the city, adjacent to Parramatta Town Hall. The Parramatta Square construction works included a redevelopment of the Parramatta Civic Centre, construction of a new culture and arts centre, and the construction of a new plaza. The designs of the first two projects, a 65-storey residential skyscraper and an office building were announced on 20 July 2012.[35] Concerns from CASA about infringements into controlled airspace from the height of the residential tower resulted in 8 Parramatta Square being turned into a 55-story commercial building, rather than the originally proposed 65-storey residential tower.[36] Parramatta Square became home to 3,000 National Australia Bank employees, relocated from the Sydney CBD.[37] Other notable commercial tenants who have established a presence at Parramatta Square include Westpac, Endeavour Energy, KPMG and Deloitte.[38]
Centenary Square, formerly known as Centenary Plaza, was created in 1975 when the then Parramatta City Council closed a section of the main street to traffic to create a pedestrian plaza. It features an 1888 Centennial Memorial Fountain and adjoins the 1883 Parramatta Town Hall and St John's Cathedral.[39]
A hospital known as The Colonial Hospital was established in Parramatta in 1818.[40] This then became Parramatta District Hospital. Jeffery House was built in the 1940s. With the construction of the nearby Westmead Hospital complex public hospital services in Parramatta were reduced but after refurbishment Jeffery House again provides clinical health services. Nearby, Brislington House has had a long history with health services. It is the oldest colonial building in Parramatta, dating to 1821.[41] It became a doctors residence before being incorporated into the Parramatta Hospital in 1949.
Parramatta is a major business and commercial centre, and home to Westfield Parramatta, the tenth largest shopping centre in Australia.[42] Parramatta is also the major transport hub for Western Sydney, servicing trains and buses, as well as having a ferry wharf and future light rail and metro services. Major upgrades have occurred around Parramatta railway station with the creation of a new transport interchange, and the ongoing development of the Parramatta Square local government precinct.[43]

Church Street takes its name from St John's Cathedral (Anglican), which was built in 1802 and is the oldest church in Parramatta. While the present building is not the first on the site, the towers were built during the time of Governor Macquarie, and were based on those of the church at Reculver, England, at the suggestion of his wife, Elizabeth.[44] The historic St John's Cemetery is located nearby on O'Connell Street.[45]


St Patrick's Cathedral (Roman Catholic) is one of the oldest Catholic churches in Australia. Construction commenced in 1836, but it wasn't officially complete until 1837. In 1854 a new church was commissioned, although the tower was not completed until 1880, with the spire following in 1883.[46] It was built on the site to meet the needs of a growing congregation. It was destroyed by fire in 1996, with only the stone walls remaining.
On 29 November 2003, the new St Patrick's Cathedral was dedicated.[47] The historic St Patrick's Cemetery is located in North Parramatta. The Uniting Church is represented by Leigh Memorial Church.[48] Parramatta Salvation Army is one of the oldest active Salvation Army Corps in Australia. Parramatta is also home to the Parramatta and Districts Synagogue, which services the Jewish community of western Sydney.[49]
The Greek Orthodox Parish and Community of St Ioannis (St John The Frontrunner) Greek Orthodox Church was established in Parramatta in May 1960 under the ecumenical jurisdiction of the Greek Orthodox Archdiocese of Australia to serve the predominantly emigrating Greek population of Greater Western Sydney. Originally, the liturgies were held in the hall of St John's Ambulance Brigade in Harris Park until the completion of the church in December 1966 located in Hassall Street Parramatta. The parish sold this property in 2014 and is now located at the corner of George and Purchase Streets.[50] The Parish Community of St Ioannis continues to serve over 5,000 Greek parishioners.[51]
A Buddhist temple is located in Cowper Street, Parramatta.[52] Parramatta's Mosque is in an apartment building on Marsden Street, Parramatta.[53] The district is served by BAPS Swaminarayan Hindu temple located on Eleanor St, Rosehill,[54] and a Murugan Hindu temple in Mays Hill, off Great Western Highway.[55]


Parramatta Park is a large park adjacent to Western Sydney Stadium that is a popular venue for walking, jogging and bike riding. It was formerly the Governor's Domain, being land set aside for the Governor to supply his farming needs, until it was gazetted as a public park in 1858.[56] As the Governor's Domain, the grounds were considerably larger than the current 85 hectare Parramatta Park, extending from Parramatta Road in the south as evident by a small gatehouse adjacent to Parramatta High School. For a time Parramatta Park housed a zoo[57] until 1951 when the animals were transferred to Taronga Zoo.
Parramatta is known as the 'River City' as the Parramatta River flows through the Parramatta CBD.[58] Its foreshore features a playground, seating, picnic tables and pathways that are increasingly popular with residents, visitors and CBD workers.[59]
Prince Alfred Square is a Victorian era park located within the CBD on the northern side of the Parramatta River. It is one of the oldest public parks in New South Wales with trees dating from c. 1869. Prior to being a public park, it was the site of Parramatta's second gaol from 1804 until 1841 and the first female factory in Australia between 1804 and 1821.
In contrast to the high level of car dependency throughout Sydney, a greater proportion of Parramatta's workers travelled to work on public transport (45.2%) than by car (36.2%) in 2016.[60]

Parramatta railway station is served by Sydney Trains' Cumberland Line, Leppington & Inner West Line and North Shore & Western Line services.[61] NSW TrainLink operates intercity services on the Blue Mountains Line as well as services to rural New South Wales. The station was originally opened in 1855, located in what is now Granville, and known as Parramatta Junction. The station was moved to its current location and opened on 4 July 1860, five years after the first railway line in Sydney was opened, running from Sydney to Parramatta Junction.[62] It was upgraded in the 2000s, with work beginning in late 2003 and the new interchange opening on 19 February 2006.[63]
The light rail Westmead & Carlingford Line runs from Westmead to Carlingford via the Parramatta city centre. A future branch will run to Sydney Olympic Park.[64]
The under construction Sydney Metro West will be a metro line run between the Sydney central business district and Westmead. Announced in 2016,[65] the line is set to open in 2032 with a station in Parramatta.[66]
Parramatta is also serviced by a major bus interchange located on the south eastern side of the railway station. The interchange is served by buses utilising the North-West T-way to Rouse Hill and the Liverpool–Parramatta T-way to Liverpool. Parramatta is also serviced by one high frequency Metrobus service:
A free bus Route 900 is operated by Transit Systems in conjunction with the state government. Route 900 circles Parramatta CBD.[67] A free bus also links Western Sydney Stadium to Parramatta railway station during major sporting events.

The Parramatta ferry wharf is at the Charles Street Weir, which divides the tidal saltwater from the freshwater of the upper river, on the eastern boundary of the Central Business District. The wharf is the westernmost destination of Sydney Ferries' Parramatta River ferry services.[68]
Parramatta Road has always been an important thoroughfare for Sydney from its earliest days. From Parramatta the major western road for the state is the Great Western Highway. The M4 Western Motorway, running parallel to the Great Western Highway has taken much of the traffic away from these roads, with entrance and exit ramps close to Parramatta.
James Ruse Drive serves as a partial ring-road circling around the eastern part of Parramatta to join with the Cumberland Highway to the north west of the city.
The main north-south route through Parramatta is Church Street. To the north it becomes Windsor Road, and to the south it becomes Woodville Road.
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 2001 | 17,982 | — |
| 2006 | 18,448 | +2.6% |
| 2011 | 19,745 | +7.0% |
| 2016 | 25,798 | +30.7% |
| 2021 | 30,211 | +17.1% |

According to the 2016 census conducted by the Australian Bureau of Statistics, the suburb of Parramatta had a population of 30,211. Of these:[69]

Parramatta is home to several primary and secondary schools. Arthur Phillip High School was established in 1960 in its own right, in buildings which had been used continuously as a school since 1875 is the oldest continuously operating public school in Parramatta. Parramatta High School was the first coeducational school in the Sydney metropolitan area established in 1913. Our Lady of Mercy College is one of the oldest Catholic schools in Australia. Macarthur Girls High School is successor to an earlier school 'Parramatta Commercial and Household Arts School'. Others schools include Parramatta Public School, Parramatta East Public School, Parramatta West Public School, and St Patrick's Primary Parramatta.

Several tertiary education facilities are also located within Parramatta. A University of New England study centre and two Western Sydney University campuses are situated in Parramatta. The Western Sydney University Parramatta Campus consists of two sites: Parramatta South (the primary site) which occupies the site of the historic Female Orphan School[72] and Parramatta North (the secondary site) which includes the adjacent Western Sydney University Village Parramatta (formerly UWS Village Parramatta) an on campus student village accommodation. Whereby, the flagship Parramatta City Campus Precinct consists of two buildings: the Engineering Innovation Hub located at 6 Hassall Street and the Peter Shergold Building located at 1 Parramatta Square (169 Macquarie Street).[73] Alphacrucis University College is a Christian liberal arts college with a campus in Parramatta located at 30 Cowper Street.[74] The University of Sydney has also announced that it intends to establish a new campus in Parramatta.[75]
The Parramatta Advertiser is the local newspaper serving Parramatta and surrounding suburbs.
On 16 March 2020, the Australian Broadcasting Corporation opened a new Western Sydney newsroom in Horwood Place at Parramatta incorporating space for 12 staff and news production equipment with the capacity to broadcast live radio programs.[76] According to the ABC, the opening formed part of its strategic goal to improve its presence in outer metropolitan areas.[76] Additionally, the ABC announced on 16 June 2021 its intention to relocate approximately 300 employees to Parramatta, which is part of a five-year plan which aims to have 75% of its content makers based away from the network's Ultimo headquarters by 2025.[77][78]


As the centre of the City of Parramatta, as well as the centre and second largest business district of Sydney, Parramatta hosts many festivals and events.[79] Riverside Theatres is a performing arts centre located on the northern bank of Parramatta River. The city hosts the following events:
Parramatta Park contains Old Government House and thus Parramatta was once the capital of the colony of New South Wales until Governors returned to residing in Sydney in 1846.[83] Another feature is the natural amphitheatre located on one of the bends of the river, named by Governor Philip as "the Crescent", which is used to stage concerts. It is home to the Dairy Cottage, built from 1798 to 1805, originally a single-room cottage and is one of the earliest surviving cottages in Australia.
The remains of Governor Brisbane's private astronomical observatory, constructed in 1822, are visible. Astronomers who worked at the observatory, discovering thousands of new stars and deep sky objects, include James Dunlop and Carl Rümker. In 1822, the architect S. L. Harris designed the Bath House for Governor Brisbane and built it in 1823. Water was pumped to the building through lead pipes from the river. In 1886, it was converted into a pavilion.[84]
Parramatta is the home of several professional sports teams. These teams include the Parramatta Eels of the National Rugby League and Western Sydney Wanderers of the A-League. Both teams formerly played matches at Parramatta Stadium that has since been demolished, and replaced with the 30,000-seat Western Sydney Stadium.[86] Parramatta Stadium was also home to the now dissolved Sydney Wave of the former Australian Baseball League and Parramatta Power of the former National Soccer League. The newly built Bankwest Stadium opened its gates for the community on 14 April 2019 with free entry for all fans. Located on O’Connell Street, the stadium is in proximity of the Parramatta CBD. The opening sporting event was the 2019 Round 6 NRL clash between Western Sydney rivals the Parramatta Eels and Wests Tigers on Easter Monday 22 April. The Eels won the match by a score of 51–6. It is being predicted that the new stadium will boost Western Sydney economy by contributing millions of dollars to it.[87]
Duran Duran's “Union of the Snake” music video with Russell Mulcahy was filmed in 1983 at Parramatta using 35mm film.[88]
The 2013 superhero film The Wolverine used the intersection of George Street and Smith Street as a filming location to depict Tokyo, Japan.[89]
Parramatta has a number of heritage-listed sites, including: